Cloud computing has significantly
transformed Human Resource Management (HRM) on a global scale, providing organizations
with scalable, affordable, and adaptable solutions. In Sri Lanka, cloud-based
HRM systems are increasingly recognized as strategic tools that enhance
operational efficiency, particularly in competitive industries like apparel,
information technology, and finance.
1. Defining Cloud
Computing in the Context of HRM
Cloud computing involves
delivering computing services—including servers, data storage, networks,
databases, and software—via the internet. This allows businesses to access HR
applications anytime and from any location (Mell & Grance, 2011).
Cloud-based HRM platforms typically support core functions such as payroll,
recruitment, training, and performance evaluation through Software as a Service
(SaaS) models.
2. Adoption Patterns in
Sri Lanka
A growing number of Sri Lankan
businesses are transitioning from conventional, on-site HR systems to
cloud-based alternatives as part of their digital transformation efforts.
Leading companies like MAS Holdings and Dialog Axiata have adopted cloud HR
solutions to efficiently manage widely distributed teams (Wijesinghe, 2022).
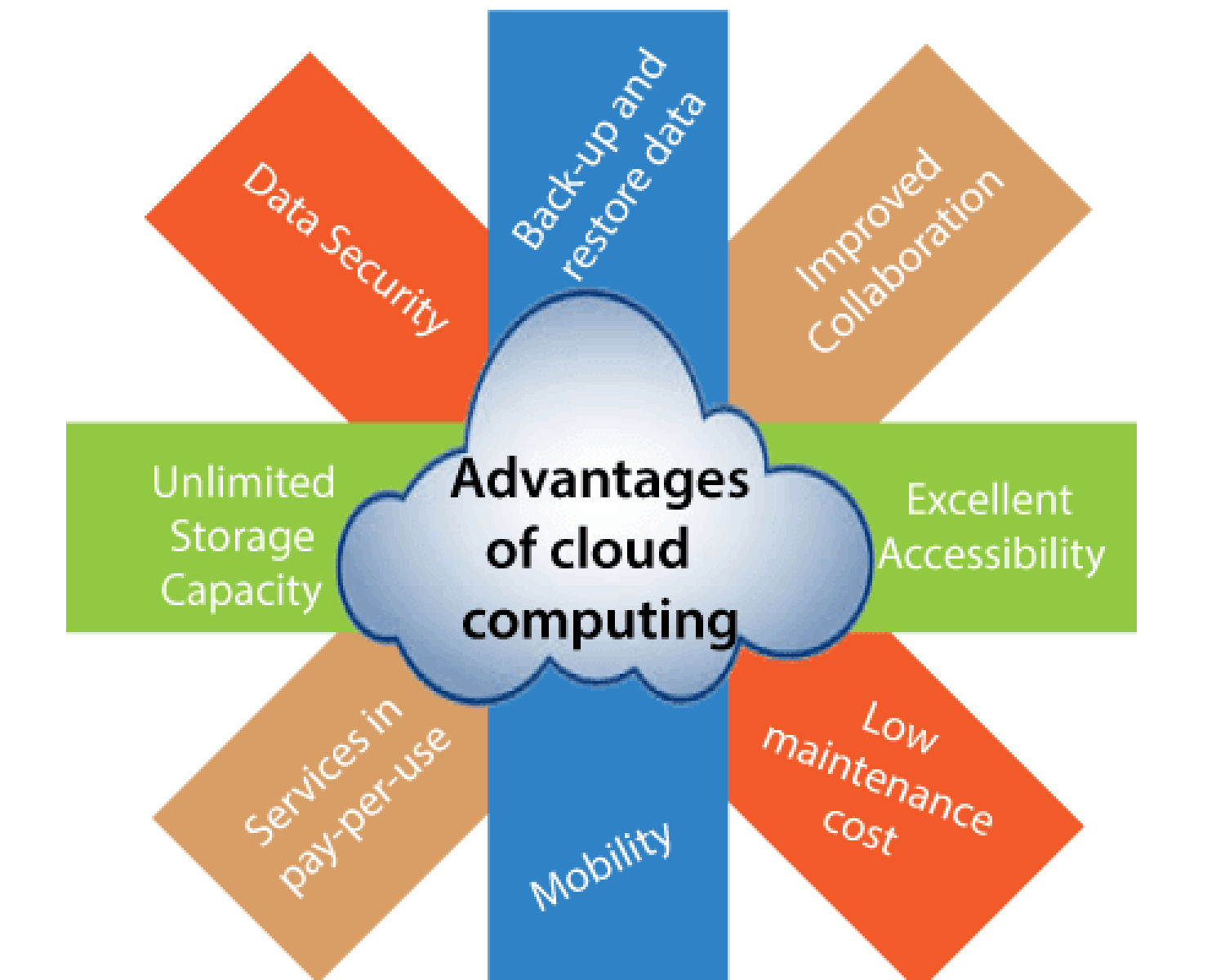
3. Advantages of Cloud
HRM in Sri Lanka
• Cost Savings: Cloud HR
platforms eliminate the need for heavy initial investments in IT infrastructure
(Gunasekara, 2020).
• Scalability: These systems
support business growth by allowing seamless expansion across regions or
countries.
• Remote Access: The ability to
manage HR functions remotely became essential during and after the COVID-19
pandemic (Fernando & Rajapakse, 2021).
• Integrated Data and Real-Time
Analytics: Cloud HRM systems offer real-time insights that support strategic HR
decisions and align them with business objectives.
4. Key Challenges
Despite the benefits, several
obstacles remain:
• Data Security Issues: Storing
sensitive HR data offsite can raise privacy and regulatory concerns.
• Resistance to Technological
Change: Cultural and organizational reluctance, especially among small and
medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), can hinder adoption (Perera, 2023).
• Limited Internet Access: Poor
internet infrastructure in rural areas affects the reliability of cloud
services.
5. Strategic
Considerations
Integrating cloud computing into
HRM allows companies to better manage talent, increase flexibility, and align
HR processes more closely with overall business strategy. It also enables
innovation in HR service delivery and reinforces HR’s role as a strategic
partner within organizations.
Conclusion
For Sri Lankan businesses,
adopting cloud-based HRM systems represents more than a tech upgrade—it is a
strategic shift. To fully realize the benefits, organizations need to invest in
upskilling their workforce, managing organizational change effectively, and
enhancing cybersecurity protocols.
References
Analytics Vidhya, 2021. Cloud computing infographic. [image online]
Available at: https://cdn.analyticsvidhya.
Fernando, S. & Rajapakse, R., 2021. Digital transformation in HRM: A Sri
Lankan perspective post-COVID-19. Journal of Management Studies, 15(2),
pp.45–59.
Gunasekara, T., 2020. The business case for cloud-based HR systems in
emerging economies: Evidence from Sri Lanka. South Asian Business Review,
11(1), pp.33–47.
Mell, P. & Grance, T., 2011. The NIST Definition of Cloud Computing.
[online] National Institute of Standards and Technology. Available at: https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/
Perera, N., 2023. Technology adoption in Sri Lankan SMEs: Opportunities and
constraints. Colombo Business Journal, 8(1), pp.22–39.
TecHRSeries, 2019. Role of Cloud in HR Management. [image online] Available
at: https://techrseries.com/wp-
Wazobia Tech, n.d. Cloud-based HR diagram. [image online] Available at: https://img.wazobia.tech/
Wijesinghe, M., 2022. Digital HRM transformation in Sri Lanka’s apparel
industry. Sri Lanka Journal of Human Resource Management, 13(1), pp.12–25.
YouTube, 2023. Digital HR transformation in organizations. [video online]
Available at: https://youtu.be/9Zvx4WbdX5s?